ACEPHAP conducts Training on Validation of New WHO Definition for Postpartum Hemorrhage
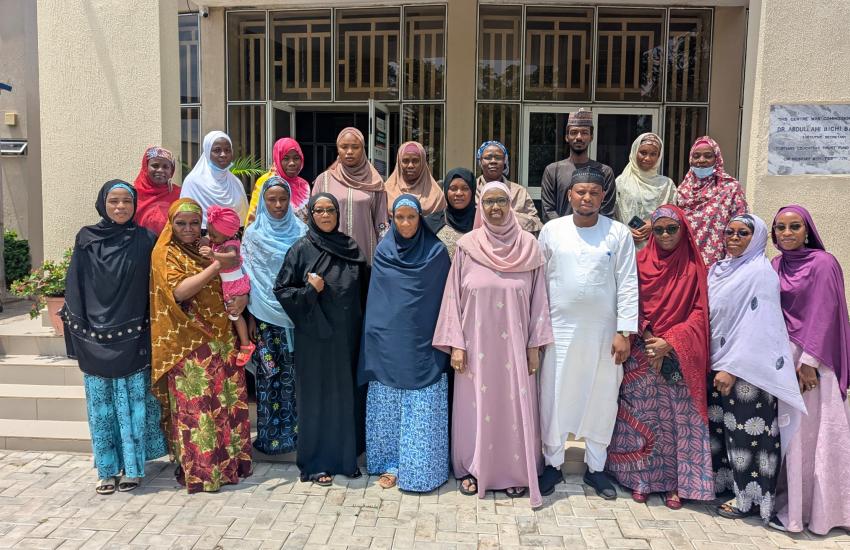
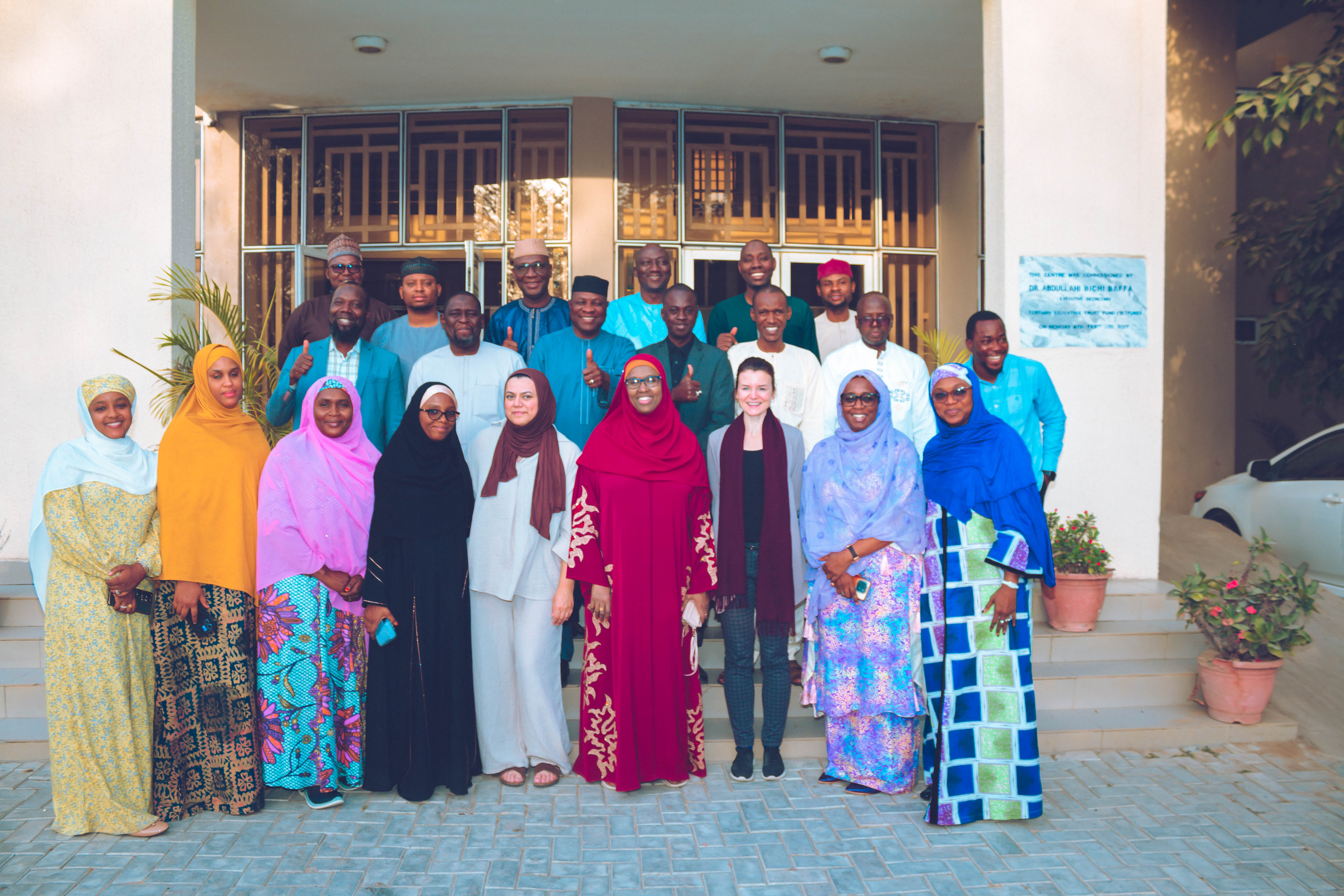
The African Centre of Excellence for Population Health and Policy (ACEPHAP) recently conducted specialized training sessions focused on validating the newly revised World Health Organization (WHO) definition of Postpartum Hemorrhage (PPH) major contributor to maternal mortality globally.
This training was conducted across all levels of healthcare; primary, secondary, and tertiary as part of a global multi-country research project aimed at testing the feasibility, acceptability, and effectiveness of the new definition in real-world settings.
Led by Professor Hadiza Galadanci, Director of ACEPHAP, the sessions provided deep insights and practical examples drawn from her extensive experience in maternal and newborn health. She emphasized the importance of adopting the updated WHO guidelines to improve clinical outcomes and reduce preventable maternal deaths.
PPH remains a critical public health issue, especially in low- and middle-income countries. Despite medical advances, delayed recognition and inadequate management continue to pose serious risks. The new WHO definition introduces objective diagnostic criteria to support early detection and prompt treatment but it must be tested outside ideal clinical trial conditions.
The project spans six countries across four WHO regions, with each country selecting three healthcare facilities representing different levels of care. Using a mixed-methods approach, the study combines direct clinical observation, qualitative interviews and cross-sectional surveys. All maternity care providers received standardized training on: the new PPH definition, objective blood loss measurement and WHO’s first-response treatment bundle
The training featured role-play, case studies, and practical demonstrations. Research assistants, trainers of trainers (TOT), and frontline workers actively engaged with the new protocols, ensuring they could confidently apply and share the knowledge within their facilities.
The primary objectives of the study are fourfold: Assess feasibility of adopting the new definition, evaluate acceptability among providers and patients, measure impact on clinical decision-making and outcomes and estimate cost-effectiveness in reducing adverse events
Participants expressed appreciation to ACEPHAP for the opportunity to enhance their skills and knowledge. With improved awareness and practical tools, they admitted that they are now better equipped to save lives and contribute meaningfully to the global goal of reducing maternal mortality.
You can join the conversation on:
- Instagram: @acephap_buk
- LinkedIn: @acephap
- Facebook: @acephap
- X/Twitter: @acephap_buk